The Plug&Charge Process in EVerest¶
This is an explaination how Plug&Charge is technically implemented in EVerest.
For a tutorial on how to do Plug&Charge in the EVerest software-in-the-loop, please refer to the Plug&Charge tutorial. For a goal oriented how-to-guide, pleaser refer to Configure Plug&Charge in EVerest.
Involved EVerest modules¶
The E2E Plug&Charge process involves communication from the EV to systems in the cloud. The main protocols involved are ISO15118 and OCPP. In EVerest, several modules and interfaces are involved in the Plug&Charge process. Here is an overview of how everything comes together in EVerest:
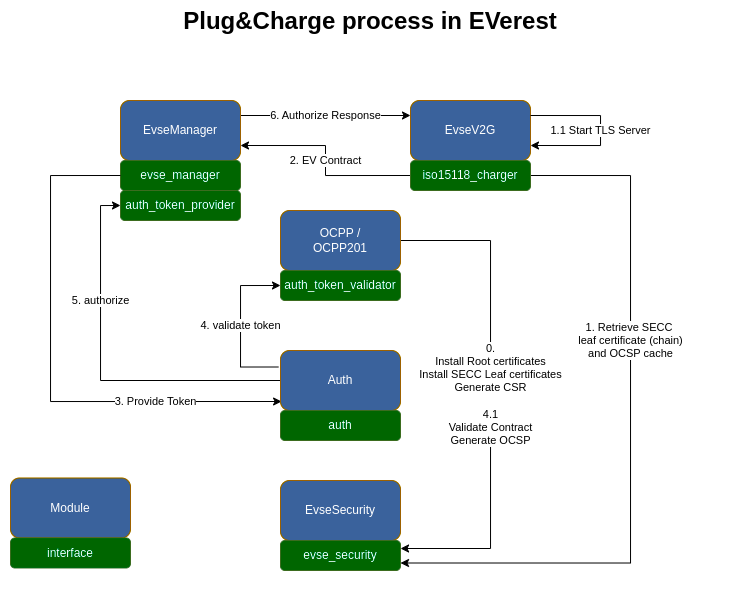
Note
This visualization only presents the interfaces and connections between them that are relevant for Plug&Charge.
Let’s have a look step by step:
Step 0¶
Before a Plug&Charge session can start, the following certificates and keys should be installed on the charger:
V2G Root certificate
SECC Leaf certificate
SECC Leaf private key
MO Root certificate (optional)
These certificates and keys can be installed during provisioning of the charger, or they can be installed using OCPP1.6 or OCPP2.x. The paths to store these files can be configured in the EvseSecurity module. Please see the Documentation of the EvseSecurity for further information on how to do the configuration for this module.
In the visualization, step (0) shows the process that represents the previously described process of provisioning the charger with the correct certificates, before there is a physical connection to the EV. The OCPP/OCPP201 and EvseV2G module require a module that implements the evse_security interface, in order to execute the following commands:
install_ca_certificate (Used by OCPP to install root certificates. This process is initiated by the OCPP CSMS)
update_leaf_certificate (Used to install or update SECC leaf certificates)
generate_certificate_signing_request (Used to generate a CSR that is used in the SignCertificate.req of OCPP)
verify_certificate (Used by EvseV2G to verify the contract certificate and by OCPP to verify new leaf certificates)
get_mo_ocsp_request_data (Used by EvseV2G and OCPP to get the OCSP request data of the contract certificate (chain))
There are more commands provided by the evse_security interface, which are not included in the Plug&Charge process.
For a successful Plug&Charge authorization process, the following certificates need to be installed on the charger:
SECC leaf certificate (including sub cas)
V2G Root Certificate(s)
MO Root Certificates(s) (only if the EV contract shall be verified locally). This can be controlled by the OCPP configuration keys described in the section OCPP 1.6 and OCPP 2.x configuration for more information.
As mentioned above, these certificates can be installed manually or by the CSMS. In case Plug&Charge is enabled and no (valid) SECC leaf certificate is installed or it expires within the next 30 days, the charging station will attempt to retrieve a SECC leaf certificate from the CSMS automatically. This process can also be triggered manually by the CSMS by using a TriggerMessage(SignCertificate).req message.
Step 1¶
This step is triggered by a physical connection between the EV and the charger. A TLS connection is required between the EV and the charger to allow Plug&Charge, so the EvseV2G module retrieves the SECC leaf certificate chain and private key from via the evse_security.yaml interface and sets up a TLS server, to which the EV can connect as a TLS client.
Step 2¶
When charger and EV have agreed on Contract being the selected payment option, we have something going on that we can call a Plug&Charge process. The EV sends its contract certificate chain and requests authorization from the charger. The EvseV2G module generates a ProvidedIdToken, which is the EVerest type that contains data about the authorization request, including the contract certificate and OCSP request data.
The ProvidedIdToken is transmitted via the evse_manager interface to the EvseManager module.
Step 3¶
The EvseManager module implements the token_provider interface and can therefore publish the ProvidedIdToken containing the contract certificate and OCSP data within EVerest to the central authorization module in EVerest: Auth.
Step 4¶
The Auth module sends commands containing the ProvidedIdToken to its registered token_validator(s), which are OCPP/OCPP201 in the case of Plug&Charge. The OCPP module(s) validate the token based on the requirements specified in the OCPP protocol (either validating locally or by the CSMS).
Step 5¶
In case the validation was successful, the Auth module notifies the EvseManager using the authorize command, that authorization is present and the charging session can be started.
Step 6¶
The EvseManager forwards the authorization response to the EvseV2G module, which can then send the awaited ISO15118 response to the EV.
Note
We have taken some shortcuts and ignored some further communication going on during the full process, but these steps cover what’s important for Plug&Charge in EVerest.
Authors: Piet Gömpel